

Periodic Table
Graphic Puzzle
"Guess the Element"
Mendeleev our Man!
|
|
|
His version of the Periodic Table

Features of the Periodic Table
arrangement of elements
horizontal rows - periods
vertical columns - group
distribution of metals and non-metals
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 H | 2 He | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 Li | 4 Be | 5 B | 6 C | 7 N | 8 O | 9 F | 10 Ne | ||||||||||
| 11 Na | 12 Mg | 13 Al | 14 Si | 15 P | 16 S | 17 Cl | 18 Ar | ||||||||||
| 19 K | 20 Ca | 21 Sc | 22 Ti | 23 V | 24 Cr | 25 Mn | 26 Fe | 27 Co | 28 Ni | 29 Cu | 30 Zn | 31 Ga | 32 Ge | 33 As | 34 Se | 35 Br | 36 Kr |
| 37 Rb | 38 Sr | 39 Y | 40 Zr | 41 Nb | 42 Mo | 43 Tc | 44 Ru | 45 Rh | 46 Pd | 47 Ag | 48 Cd | 49 In | 50 Sn | 51 Sb | 52 Te | 53 I | 54 Xe |
| 55 Cs | 56 Ba | 57 La* | 72 Hf | 73 Ta | 74 W | 75 Re | 76 Os | 77 Ir | 78 Pt | 79 Au | 80 Hg | 81 Tl | 82 Pb | 83 Bi | 84 Po | 85 At | 86 Rn |
| 87 Fr | 88 Ra | 89 Ac# |
Periodic Trends
from left to right
proton number
valency electrons
metal to non-metal
electrical conductivity
basic to acidic oxides
various 'blocks'
question
Two elements, Y and Z are in the same Period. Element Y is a non-metal. Which statement must be true for element Z?
A It
is a metal
B
It forms a basic oxide
C It
is in a different Group
D It
is a non-metal
question
The first Period consists of two elements. How many elements does the second Period consists of?
A 2
B 8
C 10
D 18
Group Features
question
Boron and aluminium are both in Group III of the Periodic Table. Which statement is true for these two elements?
A Both elements are
metals.
B Both elements
contain 3 electrons in their outermost shells.
C Both elements form
acidic oxides.
D Both elements have
the same proton number.
question
Element X forms compounds with the following chemical formulae:
MgX, H2X, CX2, Li2X
In which group of the Periodic Table would element X be placed?
A Group II
B Group IV
C Group V
D Group VI
Elements - These You Must Know!
| I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | 0 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 H | 2 He | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 Li | 6 C | 7 N | 8 O | 9 F | 10 Ne | ||||||||||||
| 11 Na | 12 Mg | 13 Al | 14 Si | 16 S | 17 Cl | 18 Ar | |||||||||||
| 19 K | 20 Ca | 24 Cr | 25 Mn | 26 Fe | 29 Cu | 35 Br | 36 Kr | ||||||||||
| 37 Rb | 53 I | 54 Xe | |||||||||||||||
| 55 Cs | 85 At | 86 Rn | |||||||||||||||
| 87 Fr |
Group I (Alkali Metals)
some visuals
|
Lithium |
Rubidium |
 |
 |
|
Sodium |
Caesium |
 |
 |
| Potassium | Francium |
 |
 |
brief intro...
1 valence electron
ions carry +1 charge
soft metals
electrical conductors
low densities
low melting points
react vigorously with cold water - alkaline solution and hydrogen gas as products
a look at this experiment
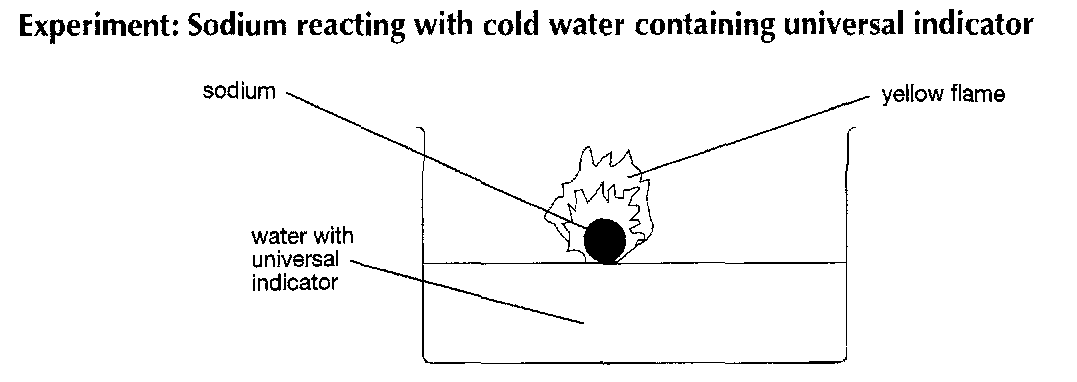
observations :
melts
burn with a yellow flame
explosion
floats
universal indicator turns blue/ purple
knowledge of equation is needed
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) --> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
changes down the group
melting points decrease
reactivity of elements increases, i.e. more vigorous reaction with water
predicting properties of other Group I elements
known properties of lithium, sodium and potassium
changes down group
| e.g. : how would Rubidium react with cold water? |
|
since sodium reacts with water as, 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) --> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) rubidium will react similarly, i.e. 2Rb(s) + 2H2O(l) --> 2RbOH(aq) + H2(g)
BUT, there is a trend down the group, elements become more reactive...
Thus the reaction of rubidium with cold water will be very explosive.
|
question
Silver (Aq) resembles Group I elements in some properties. Which property of silver is not typical of Group I?
A Silver
atoms have one outermost shell electron.
B Silver
forms a chloride with formula AgCl.
C Silver
conducts electricity.
D Silver
is resistant to corrosion by steam.
question
The elements in Group I of the Periodic Table
A are
typical metals.
B combine
with oxygen to form covalent oxides.
C form
oxides which dissolve in water to form weak acids.
D lose
electrons to form cations.
Group VII (Halogens)
some visuals
| Fluorine | Iodine |
 |
 |
| Chlorine | Astatine |
 |
 |
| Bromine | |
 |
brief intro...
seven valence electrons
ions carry a -1 charge
non-metals with low melting and boiling points
diatomic molecules
changes down the group
melting and boiling points increase
change from gas to solid
become darker in colour
less reactive - 'displacement power'
look at this experiment
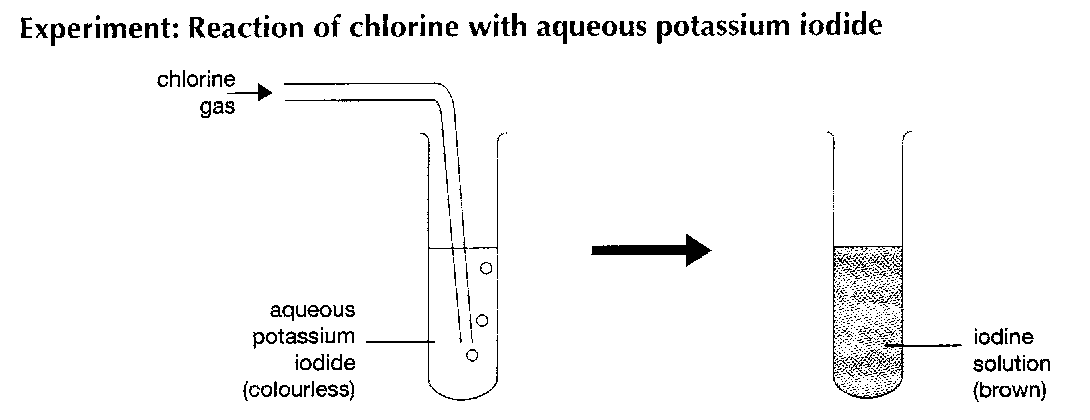
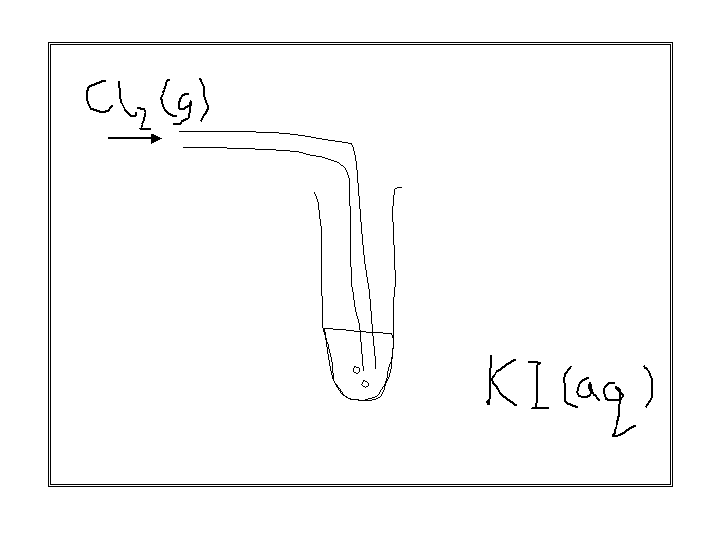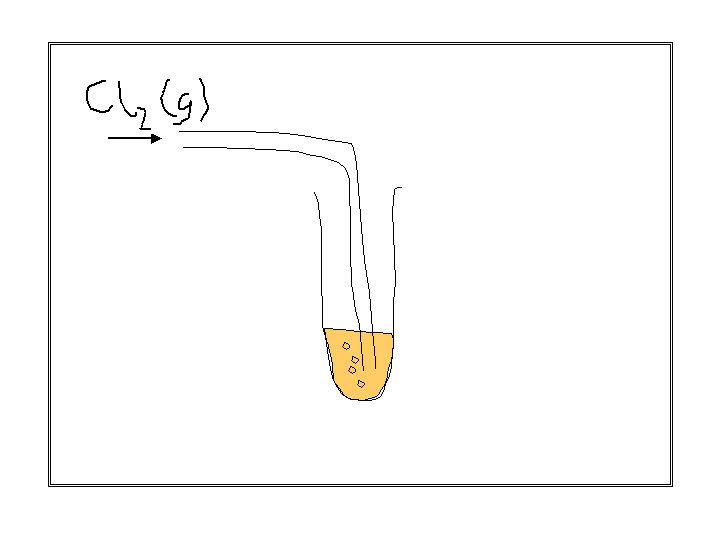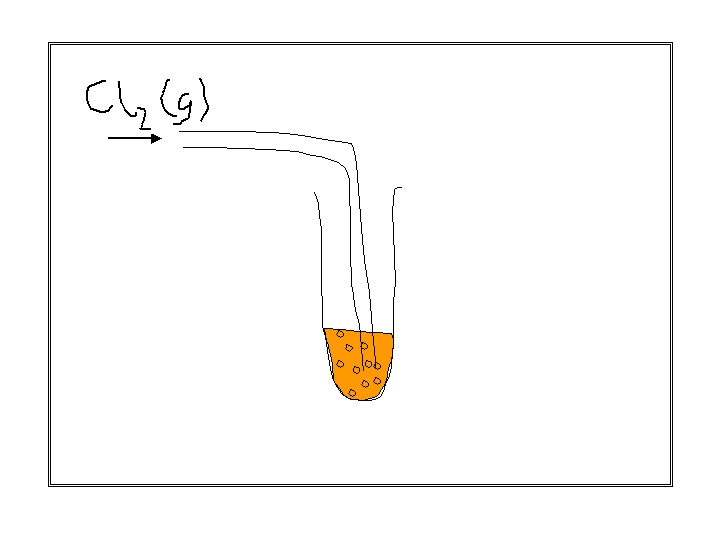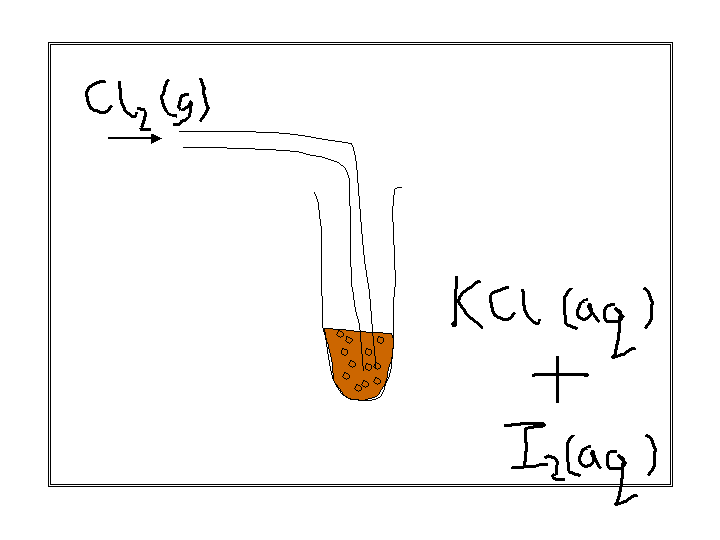
observations :
colourless solution turns brown
black solid is produced if excess chlorine is used
predicting properties of other Group VII elements
known properties of chlorine, bromine and iodine
changes down group
e.g. : Predict the physical state and colour of fluorine, above chlorine in Group VII
up the Group means that elements are lighter, therefore lower melting and boiling points
since chlorine is already a gas, fluorine with a lower melting and boiling point would be a gas also
chlorine is pale green, fluorine would be lighter - colourless maybe
fluorine will be more reactive and should displace chlorine from aqueous sodium chloride
F2 + 2NaCl --> 2NaF + Cl2
question
Fluorine is a halogen. Ar for fluorine is 19. Some properties of other halogens are given below.
| element | number of outer electrons | Mr | melting point/ °C | boiling point/ °C | colour of vapour | formula of its hydride |
| chlorine | 7 | 71 | -101 | -35 | yellow-green | HCl |
| bromine | 7 | 160 | -7 | 58 | red | HBr |
| iodine | 7 | 254 | 114 | 184 | purple | HI |
Which statement about fluorine is likely to be correct?
A The Mr
of fluorine is 38.
B Its
vapour is black in colour.
C Its
hydride has the formula FH7.
D Its
melting point in about 200 °C.
question
Astatine is the element at the bottom of Group VII. Which statement will not be true for astatine?
A
Astatine exists as diatomic molecules.
B
Astatine forms negative ions.
C
Astatine is a gas.
D
Astatine is less reactive than iodine.
question
In which arrangement of the symbols of four halogens is there an increase in reactivity from the least to the most reactive halogen?
A Br, I,
Cl, F
B Cl, F,
Br, I
C I, Br,
Cl, F
D I, Br,
F, Cl
Group O (Noble Gases)
some visuals
| Helium |
Krypton |
 |
 |
| Neon |
Xenon |
 |
 |
| Argon |
Radon |
 |
 |
unreactive gases
monatomic gases
fill air-balloons(Helium) - low density
fill light bulbs(Argon) - unreactive and so protects the filament from oxidation
question
Which one of these uses of noble gas does not depend mainly on the unreactive nature of the gas?
A Argon
used in welding
B Helium
for filling balloons
C Krypton
for electronic valves
D Xenon
for electronic flash guns
Transition Elements
some visuals
| Chromium | Copper |
 |
 |
| Manganese | Vanadium |
 |
 |
| Iron | |
 |
high densities
high melting points
coloured compounds
ions are coloured in water
variable valencies
good catalysts
-
Iron in Haber Process
- Manganese (IV) oxide in the decomposition of H2O2
question
Transition elements often form coloured compounds and have variable valencies. Which of these transition elements is an exception?
A
copper
B iron
C
manganese
D zinc
question
Which of these statements about transition elements is true?
A All
transition elements form gaseous compounds.
B
Transition elements have more than one oxide.
C
Often transition elements are coloured.
D
Transition elements have low densities.
Extra Notes
(taken from 'LETTS GCSE Revision Notes - Chemistry')



